使用定时任务
AirCode 提供了一套简单易用的定时任务。无需写任何 Cronjob 表达式,只用像在日历中安排日程一样就可以完成设置。
创建定时任务
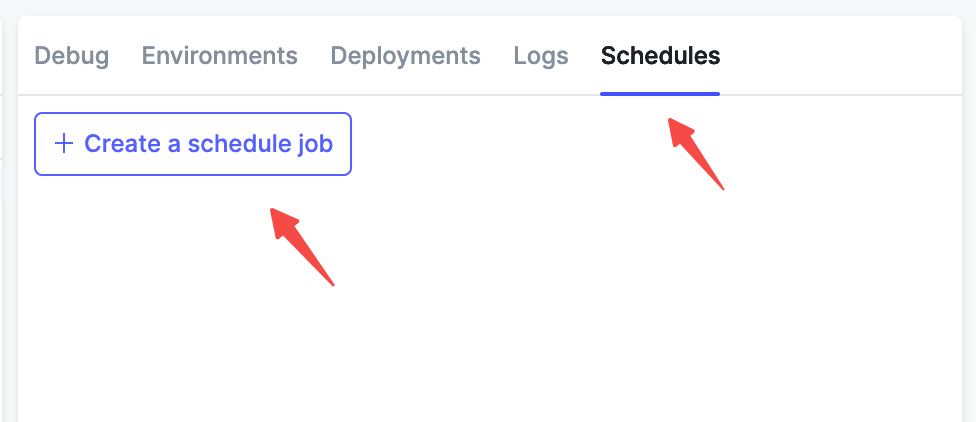
在应用页面中,进入右侧功能区中的 Schedules 标签,点击 + Create a scheduled job 按钮,即可创建一个新的定时任务。
定时任务可以在指定的时间点和时间间隔调用你的线上云函数。如果还没有创建过云函数,需要新建一个并部署。此处我们以一个简单的云函数为例:
module.exports = async function(params, context) {
console.log('You should drink water now.');
return;
}
module.exports = async function(params, context) {
console.log('You should drink water now.');
return;
}
提醒
定时任务只能调用线上部署的云函数,因此需要先部署,参考部署云函数。
部署后,在创建定时任务的弹窗中就可以完成相关配置并点击 Add 按钮完成新增。

- Job Name:定时任务的名称,主要用于标识,可以自定义
- Start Time:定时任务第一次执行的时间,如果该时间已过,则会根据重复规则在下一次执行
- Functions to Run:定时任务要调用的云函数,可以选择多个,选择多个时会同时执行,没有时序关系
- Repeat Type:定时任务的重复规则,可以选择 No Repeat、Minute、Hour、Day 等
- Repeat Interval:定时任务的重复间隔,可以选择 1、2、3 等
- End Time:定时任务的结束时间,如果不设置,则默认为永久重复
查看执行日志
在功能区的 Logs 标签中,可以查看定时任务的执行日志。通过定时任务执行的云函数会带有 [SCHEDULE] 的前缀。

超时时间
定时任务执行云函数时,函数的执行超时时间与该应用的超时时间一致,超过该时长的任务将会被提前终止执行。如果需要修改超时时间,可以在应用的设置中修改。参考云函数运行时 - 超时时间。
限定函数仅由定时任务触发
如果希望限定某个云函数只能由定时任务触发,可以使用 context.trigger 来判断触发方式,这可以避免被 HTTP 的方式误触发。
module.exports = async function(params, context) {
if (context.trigger !== 'SCHEDULE') {
console.log('This function is not called by a scheduled task.');
return;
}
// Do something...
}
module.exports = async function(params, context) {
if (context.trigger !== 'SCHEDULE') {
console.log('This function is not called by a scheduled task.');
return;
}
// Do something...
}
关于 context.trigger 的完整定义,参考云函数 API - context.trigger。
传递调用参数
定时任务本身只是一个定时执行器,它并不会传递任何参数给云函数,因此通过定时任务调用的云函数中 params 为空。若希望传递参数,可以在执行的云函数中调用其他云函数,并在调用时传参。
例如,有一个需要参数的云函数 functionNeedParams:
module.exports = async function(params, context) {
return { params };
}
module.exports = async function(params, context) {
return { params };
}
在真正被执行的云函数中,调用 functionNeedParams 并传递参数即可:
const aircode = require('aircode');
// Load the functionNeedParams
const functionNeedParams = require('./functionNeedParams');
module.exports = async function(params, context) {
// Call functionNeedParams with params
const result = await functionNeedParams({ foo: 'bar' }, context);
// If the params are variable, you can store them in the db first,
// then retrieve and pass them
const MyParamsTable = aircode.db.table('myParams');
const dbParams = await MyParamsTable.where().findOne();
const anotherResult = await functionNeedParams(dbParams, context);
return;
}
const aircode = require('aircode');
// Load the functionNeedParams
const functionNeedParams = require('./functionNeedParams');
module.exports = async function(params, context) {
// Call functionNeedParams with params
const result = await functionNeedParams({ foo: 'bar' }, context);
// If the params are variable, you can store them in the db first,
// then retrieve and pass them
const MyParamsTable = aircode.db.table('myParams');
const dbParams = await MyParamsTable.where().findOne();
const anotherResult = await functionNeedParams(dbParams, context);
return;
}
通过自定义间隔执行
AirCode 提供了一些常用的执行间隔,例如每周、每天、每分钟、每 5 分钟等。如果需要更灵活的执行间隔,可以通过设置一个常用间隔,并在代码中判断执行的方式来实现。
例如,希望实现一个每 2 天执行一次的定时任务,可以先设置一个每天执行的定时任务,然后在代码中判断当前时间是否是偶数天:
const aircode = require('aircode');
module.exports = async function(params, context) {
// Get the count of days from the db
const DaysCountTable = aircode.db.table('daysCount');
const daysCount = await DaysCountTable.where().findOne();
// Update the count of days, or save a new one
if (daysCount) {
daysCount.count = count + 1;
await DaysCountTable.save(daysCount);
} else {
await DaysCountTable.save({ count: 1 });
}
// If the count of days is odd, return
const count = daysCount ? daysCount.count : 0;
if (count % 2 !== 0) {
return;
}
// Do something...
}
const aircode = require('aircode');
module.exports = async function(params, context) {
// Get the count of days from the db
const DaysCountTable = aircode.db.table('daysCount');
const daysCount = await DaysCountTable.where().findOne();
// Update the count of days, or save a new one
if (daysCount) {
daysCount.count = count + 1;
await DaysCountTable.save(daysCount);
} else {
await DaysCountTable.save({ count: 1 });
}
// If the count of days is odd, return
const count = daysCount ? daysCount.count : 0;
if (count % 2 !== 0) {
return;
}
// Do something...
}