在线开发云函数
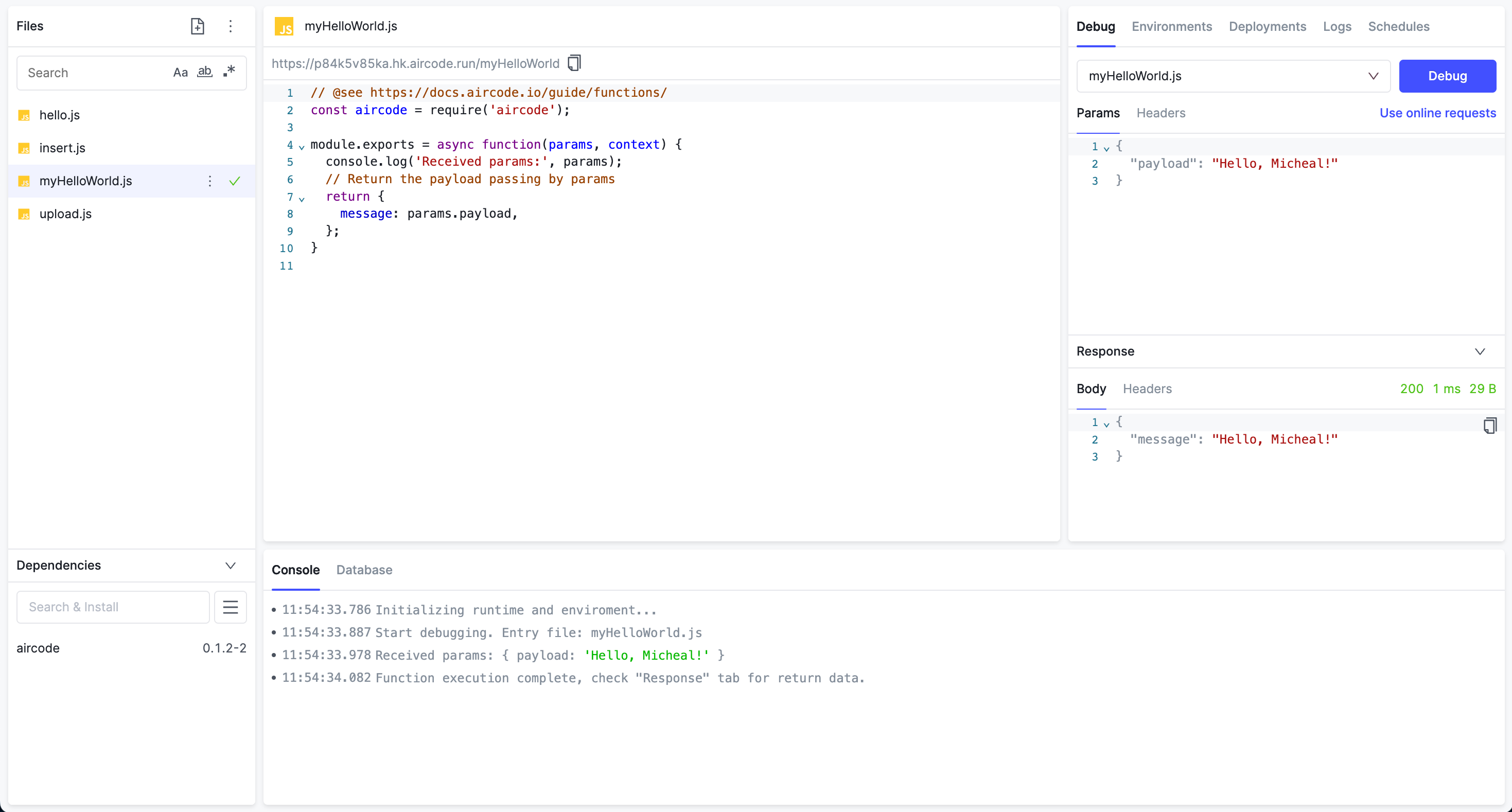
AirCode 提供了一个 WebIDE,让云函数的开发过程完全在线完成,无需下载任何软件和配置。
运行环境
AirCode 的云函数使用 JavaScript 作为编程语言,运行时环境为 Node.js。
若你对这两项技术感到陌生,建议先通过 JavaScript Tutorial 和 Node.js 官网 进行学习。
创建云函数
点击函数列表中的 + ,输入函数名称,点击 ✓ 就可以创建一个 Node.js 云函数。
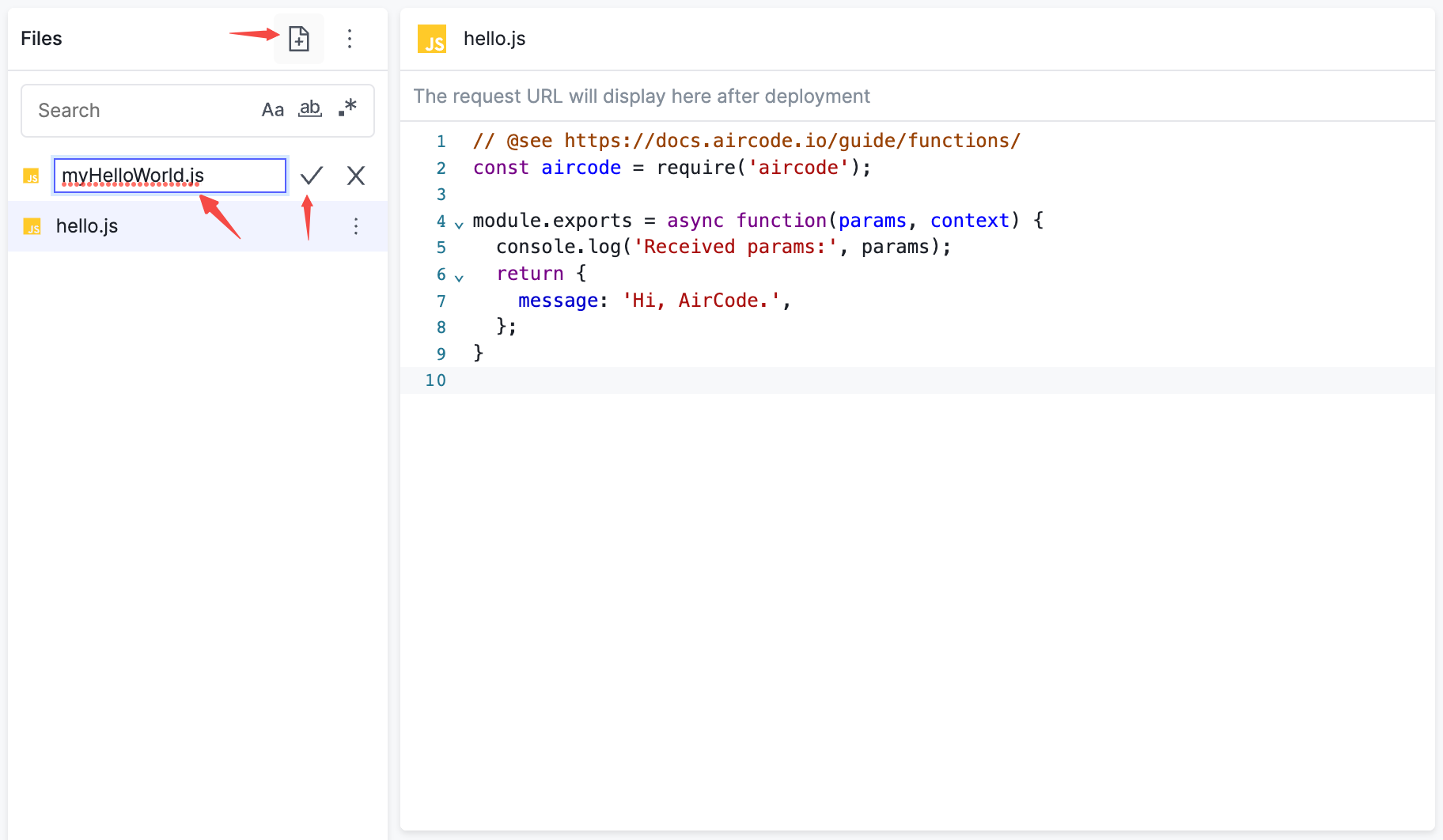
所有云函数都以 .js 作为扩展名,你也可以修改扩展名来创建其他类型的文件,例如 .json 文件、.txt 文件等。这些非 .js 的文件将不会被当做云函数,即不会生成线上 URL 接口。它们一般用于存储配置信息,并在其他云函数中通过 require 引用。
函数模板和参数
module.exports = async function(params, context) {
return {
message: 'Hi, AirCode.',
};
}
module.exports = async function(params, context) {
return {
message: 'Hi, AirCode.',
};
}
每个云函数都需要 module.exports 一个 async 函数,这个函数包含 params 和 context 两个变量。
params是请求函数时携带的参数context包含请求时的上下文信息以及一些辅助方法
注意
如果没有通过 module.exports 导出一个 async 函数,则该云函数将无法被线上请求。这一般会被用于私有函数,更多细节请参考:私有函数。
示例:
module.exports = async function(params, context) {
return {
message: params.message,
method: context.method,
};
}
module.exports = async function(params, context) {
return {
message: params.message,
method: context.method,
};
}
上线后通过 curl 访问该函数,并携带请求体:
curl -H "content-type:application/json" -X POST -d '{"message": "Hello World"}' \
https://sample.hk.aircode.run/hello
curl -H "content-type:application/json" -X POST -d '{"message": "Hello World"}' \
https://sample.hk.aircode.run/hello
会得到如下结果:
{
"message": "Hello World",
"method": "POST"
}
{
"message": "Hello World",
"method": "POST"
}
更多参考
- 了解如何通过
params获取 POST 参数和 GET 参数 - 了解如何通过
context获取和设置上下文
函数返回
每一个云函数的导出函数都需要有返回值,这个值会被作为 Response Body 返回。
注意
应该避免在返回值中包含循环引用,否则会造成输出错误。
处理异步任务
因为导出函数为一个 async 函数,我们推荐使用 await 来处理异步任务,例如 HTTP 请求、Promise 任务等。
module.exports = async function(params, context) {
// A sleep function return a Promise task
const sleep = ms => new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, ms));
// Use `await` to handle the asynchronous tasks
await sleep(1000);
return {
message: 'Hello after sleeping 1 second',
};
}
module.exports = async function(params, context) {
// A sleep function return a Promise task
const sleep = ms => new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, ms));
// Use `await` to handle the asynchronous tasks
await sleep(1000);
return {
message: 'Hello after sleeping 1 second',
};
}
注意
因为云函数底层是 Serverless 的,若没有使用 await 来等待异步任务结束,则异步任务会在函数返回后被中断而无法继续执行,结果也是不可预知的。
例如:
module.exports = async function(params, context) {
setTimout(() => {
// This text won't be logged
console.log('A log in async task');
}, 1000);
// After return, the setTimeout async task will be terminated
return {
message: 'Hi, AirCode.',
};
}
module.exports = async function(params, context) {
setTimout(() => {
// This text won't be logged
console.log('A log in async task');
}, 1000);
// After return, the setTimeout async task will be terminated
return {
message: 'Hi, AirCode.',
};
}
处理函数错误
推荐使用 try catch 来处理函数中出现的错误,例如:
module.exports = async function(params, context) {
// Use `try catch` to handle errors
try {
const result = await someTask();
return {
result,
};
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error happened.');
return {
error: error.message,
};
}
}
module.exports = async function(params, context) {
// Use `try catch` to handle errors
try {
const result = await someTask();
return {
result,
};
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error happened.');
return {
error: error.message,
};
}
}
如果函数运行过程中出现了没有被捕获的错误,则会返回 500 Internal Server Error。
更多参考
函数中的时区问题
无论应用部署在哪个区域,AirCode 云函数中的时区均为 UTC±0。若对时区有自定义需求,可使用 dayjs 库。
// Require `dayjs` and its plugins to support custom timezone
const dayjs = require('dayjs');
const utc = require('dayjs/plugin/utc');
const timezone = require('dayjs/plugin/timezone');
dayjs.extend(utc);
dayjs.extend(timezone);
module.exports = async function(params, context) {
const date = new Date();
// The default timezone is UTC±0
const defaultTimezone = date.toLocaleString();
// Use dayjs to set a custom timezone
const customTimezone = dayjs(date).tz('Asia/Shanghai').format('YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss');
return {
defaultTimezone,
customTimezone,
};
}
// Require `dayjs` and its plugins to support custom timezone
const dayjs = require('dayjs');
const utc = require('dayjs/plugin/utc');
const timezone = require('dayjs/plugin/timezone');
dayjs.extend(utc);
dayjs.extend(timezone);
module.exports = async function(params, context) {
const date = new Date();
// The default timezone is UTC±0
const defaultTimezone = date.toLocaleString();
// Use dayjs to set a custom timezone
const customTimezone = dayjs(date).tz('Asia/Shanghai').format('YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss');
return {
defaultTimezone,
customTimezone,
};
}
避免使用全局变量
AirCode 的底层运行时多实例的,且会根据请求量实时动态扩缩容,无法保证每一次请求都访问到同一个实例中。因此,应该尽量避免使用全局变量来保存值,因为这将导致不符合预期的结果。
例如:
// Using global variables can lead to unexpected results
let someGlobalVar = 0;
module.exports = async function(params, context) {
// The original value of `someGlabalVar` is unpredictable
someGlobarVar += 1;
// An unexpected return value
return {
someGlobarVar,
};
}
// Using global variables can lead to unexpected results
let someGlobalVar = 0;
module.exports = async function(params, context) {
// The original value of `someGlabalVar` is unpredictable
someGlobarVar += 1;
// An unexpected return value
return {
someGlobarVar,
};
}
若对于函数中有全局变量存储需求,建议使用数据库,参见:数据库入门。
删除云函数
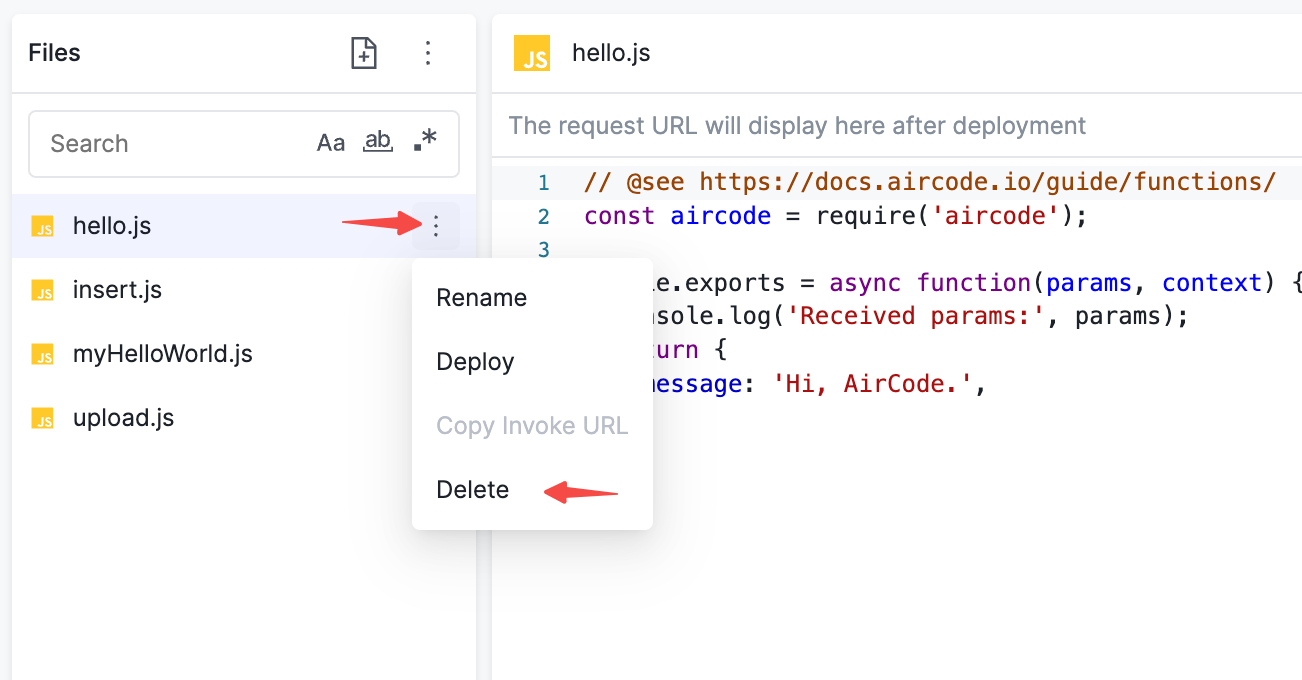
点击函数列表中对应函数的更多按钮,选择 Delete ,在弹出对话框中点击确认即可删除该函数。
更多参考
- 如果删除的这个函数已经上线过,则需要再执行一次部署才能从线上将其删除,参考:部署云函数 - 部署删除操作
- 删除后的云函数会被放到函数回收站,可以查看和恢复,参考:函数回收站